Positive Attitude
There are a remarkable number of studies in the academic literature that have shown that having a positive attitude toward aging is beneficial for a variety of things. For seniors, a good attitude toward aging can positively affect our quality of life, our sense of wellbeing and our longevity. Having a positive attitude toward aging can even reduce the risk of dementia1 as we age.
But day-to-day activities are also affected by our attitudes. One such activity is how we approach learning new skills, in particular, the technologies that are now so prevalent in our daily lives.
The American Psychology Association (APA) makes the following point:
The technological revolution has made it almost impossible to separate how we conduct our social lives, business, healthcare and education from the technology that allows us to do so. With vast information flowing to and from our fingertips, the way people interact with the world has fundamentally changed.
In a previous blog, I talked about the importance of staying connected with the friends and family that make up our social network. These connections are vital to reducing the risks of loneliness, which can lead to depression, but equally important are the positive effects they have on our brain health.
We all strive to maintain our social networks, but that looks very different for seniors in 2020 than it did for our grandparents. As the American Psychological Association points out, more and more, technology is used to stay connected with others, and mastering this new technology can often be a challenge for us seniors. When it comes to our willingness to embrace technology, having a positive attitude can help us improve our self-confidence and perceived self-efficacy.
Attitude, Anxiety and Self-efficacy
Let’s talk about self-efficacy. Self-efficacy is not the same as self-confidence. The APA defines perceived self-efficacy as: “An individual’s subjective perception of his or her capability for performance in a given setting or ability to obtain desired results”. If we believe that we can learn something new and valuable, we are more likely to try to master that behavior. This is where self-efficacy comes in. If you believe you can do something you are more likely to try it and be successful at it.
On the other hand, if we are anxious2 when we approach a new learning experience, we are much more likely to struggle to learn and much more likely to give up if we feel confronted by potential difficulty3. Having a positive attitude about life and aging makes us more likely to view new experiences as surmountable challenges rather than insurmountable barriers. Having a positive attitude creates a greater probability of experiencing perceived self-efficacy, resulting in greater willingness to take on new learning experiences.
Technology
Many older people are intimidated by technology. Probably because we didn’t grow up with it. However, technology is especially important for seniors. One study described the importance of web-based learning for older adults. “Web-based health information is particularly important for the increasing number of older adult online users. One strategy to deliver synthesized, evidence-based health information to these individuals is through Web-based learning modules.”
Another study drew similar conclusions. They described trends in the field of healthcare, specifically for an elder population including the rapid pace of technological development, the unprecedented growth in the aging population, and the growing and unsustainable cost of caring for the aging population. They see the use of technology for patient education as a means of getting ahead of these trends:
So, it is important that we be able to use technology to help us manage our interface with personal healthcare providers. Also, as mentioned earlier, it is important that we be able to use technology to maintain our social interaction with others as well as for capitalizing on the many benefits associated with technology.
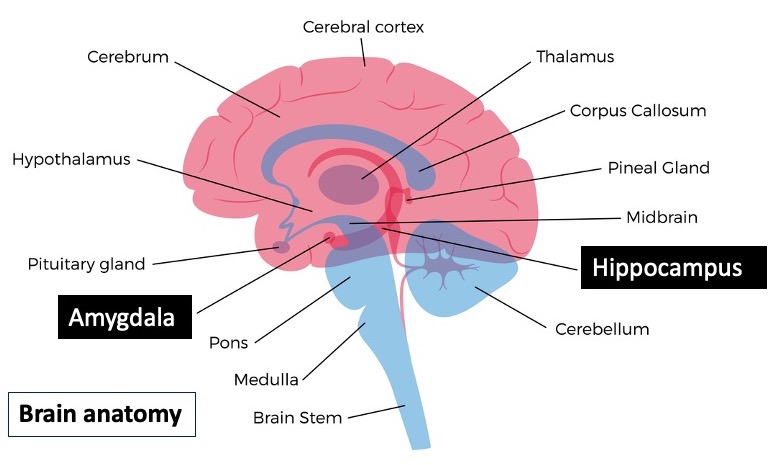
In my last blog I discussed the aging brain and how our memory works. I discussed the importance of the hippocampus for creating long term memories. When I looked at positive attitude and how it affects our self-efficacy and hence our potential for learning new technology, I found an interesting study that talks about the relationship between a positive attitude and learning:
We found that positive attitude was associated with increased engagement of the hippocampal learning-memory system…increased hippocampal activity and more frequent use of efficient memory-based strategies mediated the relation between positive attitude and higher math achievement. Our study is the first to elucidate the neurocognitive mechanisms by which positive attitude influences learning and academic achievement.
What’s in it for You?
In the case of attitude change, there are myriad theories on how best to create change in our attitude. Offering you advice on how best to do this is somewhat difficult. There are a couple of theories that we can work with to help us change our attitude and hence our perceived self-efficacy toward the adoption of more technology. But before we look at possible strategies for changing our attitude let’s explore some of the many reasons why it would serve us well to adopt a more positive attitude toward exploring and using technology.
Social Media. Instagram, Tik Tok, Facebook, and Twitter are just a few examples of social media applications. These applications are excellent for staying in touch with friends and family. Facebook, for example, can allow you to share photos and comments with others and gives you a chance to comment on material posted by your friends. Social media is very popular with younger people, but it can have a very positive effect on seniors looking to stay in touch and share life experiences with family and friends.
Tools. Electronic Calendars, Email, Skype, Zoom,. These tools are excellent for staying in touch with friends and family, and a no-cost way to see interact with grandchildren, even those living halfway around the world. Zoom, of course, is extremely important for almost everyone given our current struggles with the pandemic. Business, social groups, and individuals are using Zoom and other web-based conferencing applications for creating and supporting groups of people talking and interacting face-to-face online. What better way to have a weekly meeting with family and friends than to schedule a Zoom call? I know people who read bedtime stories to their grandchildren on Zoom.
Shopping. Amazon, Instacart, eBay, and Etsy. Online shopping is here to stay. Most retailers now offer an online shopping app. Online shopping has become so popular and necessary, that some brick and mortar retailers are going out of busines or switching over to online sales only. Grocery shopping is also accessible via technology. Using a computer or a smart phone, you can order your groceries to be delivered from places like Whole Foods, Costco, or your neighborhood grocer via the Instacart app. This can be a lifesaver for those with mobility issues.
Online learning. TEDTM Talks, One Day University, Udacity, YouTube, Museums, and National Geographic and Websites for research and exploration. Online learning is very important to me. I use it all the time, and I taught psychology online for over ten years at the University of Phoenix. I can’t tell you how many hours I’ve spent online watching YouTube videos and TED Talks. (If you ask my wife, too much time.) I have even toured museums and traveled to many foreign places online.
Messaging. Smartphones, WhatsApp, and Facetime. Smartphones are a standard accessory and tool in modern life. If you don’t have a modern smart phone there are many for sale on eBay for as little as $100.00. Many people use the texting feature on their smartphone. It has become an international obsession. Texting is a great way of connecting instantly with friends and family. It has almost taken over from making phone calls. My cleaning ladies, dentist, and dog groomer use text messages to remind me of appointments and when to pick up my dog.
Wellness. Medical Interfaces, Meditation apps, Exercise apps for seniors. As described above, there are opportunities for seniors with some basic technological skills to interface directly with their healthcare providers. I belong to a large healthcare organization in Northern California that allows me to login to my online account and review notes written by my primary care physician or any specialists I may have visited. The notes are a recap of what was said or discovered during that visit. This is becoming an even greater trend for more and more medical professionals going forward. And my wife uses a meditation app on her smartphone, a practice which greatly affects her mood and attitude.
So now what? We have seen that a positive attitude can have a significant effect on how we age. We’ve seen that a good attitude can help us create better perceived self-efficacy and that can help us improve our relationship with an important element of our life, technology. We’ve explored some of the benefits of utilizing technology. Now we need to look at some possible ways to shape our attitudes and create an interest in technology.
Attitude Change
If your attitude in general, and your attitude toward technology in particular, needs adjusting, let’s look at some ways we might be able to work on it.
Attitude change advice is hard to offer since the strategies for creating attitude change typically involve forces from outside the person who is needing to change their attitude. In the academic literature there are numerous theories on how people develop and change their attitudes. A couple of theories I have been familiar with since college are cognitive dissonance theory and self-perception theory.
I don’t want to spend a lot of time on theoretical stuff, but I want to maintain some degree of academic integrity, so I need to acknowledge the authors of these theories. Dissonance theory was first proposed by Leon Festinger in 1957. It has become part of our vernacular. I’ve seen it and heard it in popular media. Self-perception theory was first proposed by Daryl Bem in 1972. Self-perception theory has been used in the context of psychotherapy for many years.
These theories basically say: Go and do what you think you’re not good at, and the fact that you are doing it will cause you to change your beliefs or attitude about that behavior. Instead of the usual method of changing behavior which is to change our thoughts about something which will lead to a change in behavior, instead we need to engage in that behavior to change how we think about it. This is the reverse of how we usually think about attitude change. Sounds great in theory but how do we get ourselves to begin to interact in a meaningful way with something we have no perceived self-efficacy toward?
As I see it, there are three thing we need to do. First let’s look at our self-talk. When we think about approaching technology what do we say to ourselves? Maybe it’s something like: Oh my God I can’t do this, this will never work, I’m too old to learn this, people will make fun of me when I can’t do it, people will think I’m dumb. None of those things are true! Let me share a personal story that illustrates my point.
I enrolled in a PhD program in 2001. I was 53 and apparently one of, if not the oldest freshman ever to enroll in the organizational psychology program at the university. I went to orientation and bought all the books (they were still using real books back then). I took a large stack of books home and decided to read through a couple of them. The first book I picked up was The Conduct of Inquiry by Abraham Kaplan. I started to read it. Chapter one page one. I read about half a page but wasn’t sure what I read. The language and writing style seemed odd and convoluted to me. So I reread the page several times and still didn’t understand what he was saying. I panicked! I mean really panicked. I got a knot in my stomach and started to sweat. I had the overwhelming realization that I was too old to be in a PhD program. My brain was too old, and I had been out of school too long. I wanted to drop out. My wife was out of town, so I called her and told her what happened and that I wanted to quit. She talked me through it, and I agreed to give it a chance. I went to class the first day and my entire cohort, made up of students much younger than me, was complaining about that very same book. We all thought it was bizarrely written and unreasonably difficult to understand. Long story short, I struggled through the book and passed the class, and went on to earn my PhD. That is an example of how negative self-talk can influence our prospects for achieving success.
In this example I didn’t talk myself into believing I would be successful, and I didn’t change my attitude toward the rigors of the program. I just agreed to take on the challenge, even if I failed. I stopped saying “I can’t do this” and started saying “I’ll do the best I can”.
This brings us to the second step in changing our attitude, which is to actually engage in the behavior we want to avoid. If you can clean up your self-talk long enough to get yourself engaged in the behavior you need to engage in, you have the opportunity to create that cognitive dissonance. If you are actually working on a computer or texting on a cell phone, then it will be difficult for you to believe that you can’t do it, since you are actually doing it and gradually becoming more proficient. Your attitude will change, and you will accept the new reality that you can use technology in a productive manner.
Of course, there is still the leap from zero to something. The best way to manage this is with the support of others. Instead of avoiding taking that computer class for seniors at the community center just sign up and show up. As the saying goes, 80% of success in life is just showing up.
Here is a link to an excellent website Senior Planet that offers a number of excellent self-help videos on a variety of computer and cell phone applications. You can use sites like these to get you started to help you adjust your attitude by realizing that you are in fact using technology.
Once you get even the smallest amount of success you can move to the third stage in creating a new and improved attitude toward technology. Acknowledge yourself!
This takes us back to the cognitive component of attitude change. Once you learn to do something, use positive rather than negative self-talk. Avoid saying things like: “Well, anybody could have learned that” or “That was simple, I can’t do the complex things,” etc.
Look at what you have accomplished and acknowledge yourself. Try saying, “That was awesome, I’m on my way” or “Good first step, I’m committed to learning this”.
This is how you make the change in your attitude. By doing!
Endnote: Some of the references used in researching this blog were found on a commercial digital library site (ProQuest). Because many readers cannot access them by hyperlink, I am giving the reference citation in case someone wants to look them up.
References
1 Positive attitudes about aging reduce risk of dementia in older adults. (2018, Feb 07). Targeted News Service
2. Bandura, A., Reese, L., & Adams, N. E. (1982). Microanalysis of action and fear arousal as a function of differential levels of perceived self-efficacy. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 43(1), 5–21.
3.Taylor, J. A., & Spence, K. W. (1952). The relationship of anxiety level to performance in serial learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 44(2), 61–64.

Ed Lopez, PhD, Love of Aging’s Science Editor is a retired organizational psychologist, university instructor and researcher. His research has been presented at international conferences and published in a peer reviewed journal. Ed is also a decorated Army veteran who served in Vietnam.